Cookies & Your Privacy
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. More Information >
Home » Learning & Resources » Case Studies » Retaining Wall Stabilization
A deteriorating bin-type retaining wall at an industrial facility in Alaska was exhibiting significant structural distress. Corrosion of the steel facing had led to localized soil loss and visible outward movement of the wall. Because the wall retained footings that supported critical site infrastructure, removal and replacement were not viable. Additionally, the presence of asbestos in the wall facing restricted mechanical repair options and necessitated a minimally invasive stabilization method.
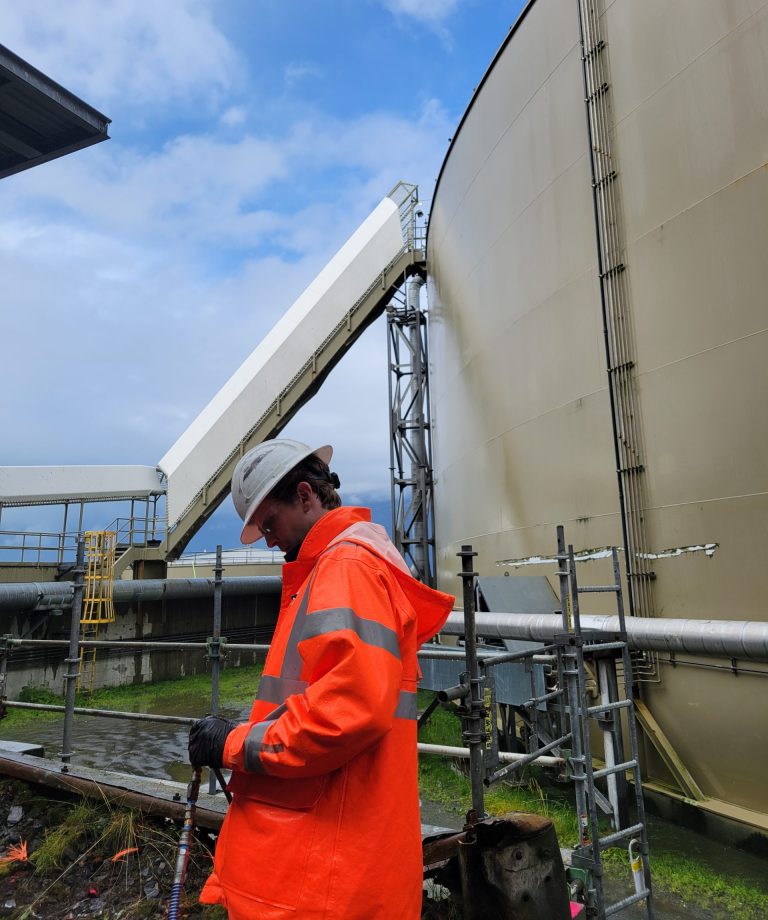

Working collaboratively with the site’s engineering team, a two-stage polyurethane grouting plan was developed to stabilize the retained soils and prevent further wall movement. The approach combined two distinct polyurethane foam products, each selected for its unique physical properties and suitability for specific subsurface conditions.
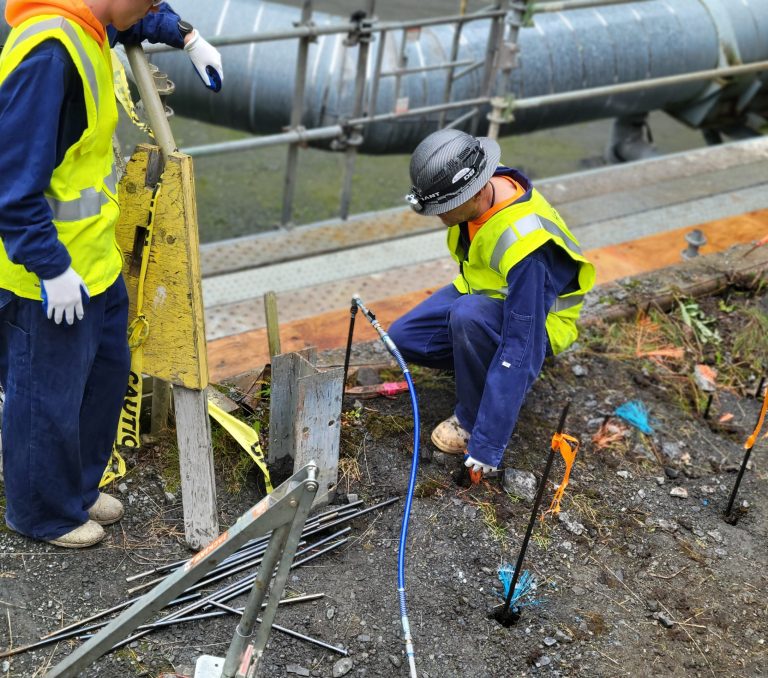

Near-Wall Treatment – HS010 Single-Component Foam: The initial phase involved injection of HS010, a low-expansion, single-component polyurethane foam, via permeation grouting directly behind the corroded wall facing. This material was chosen for its ability to:
Subgrade Reinforcement – HF402 Dual-Component Foam: In the second phase, HF402, a high-expansion, dual-component polyurethane foam, was injected at greater distances from the wall. This grout provided:
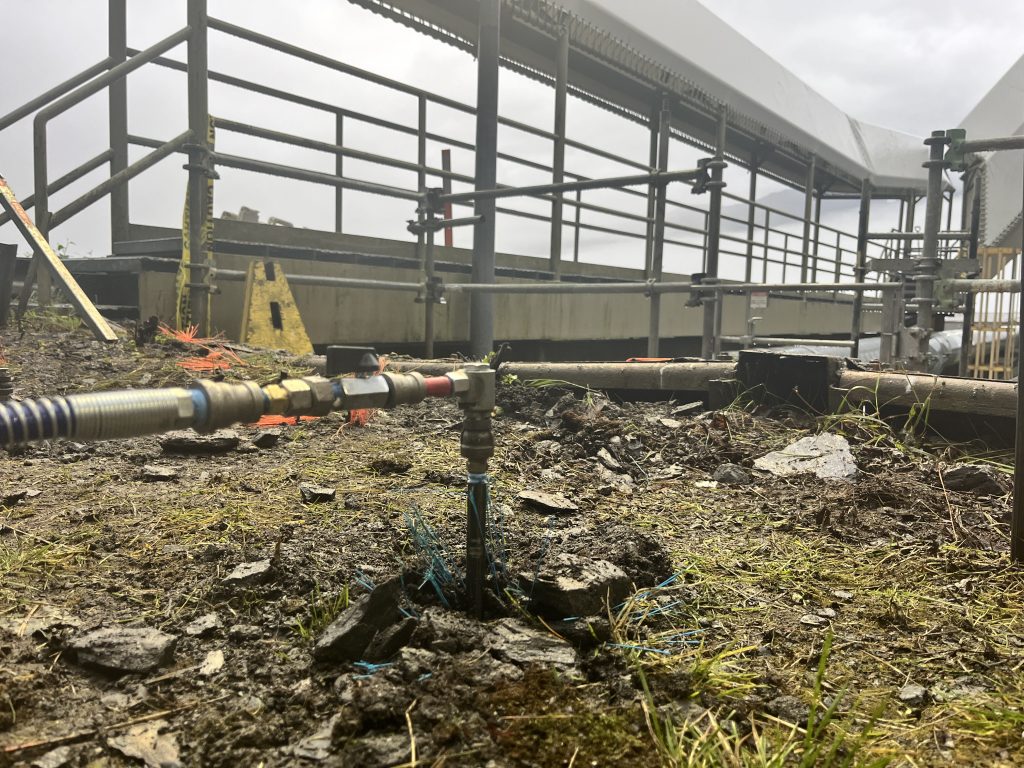
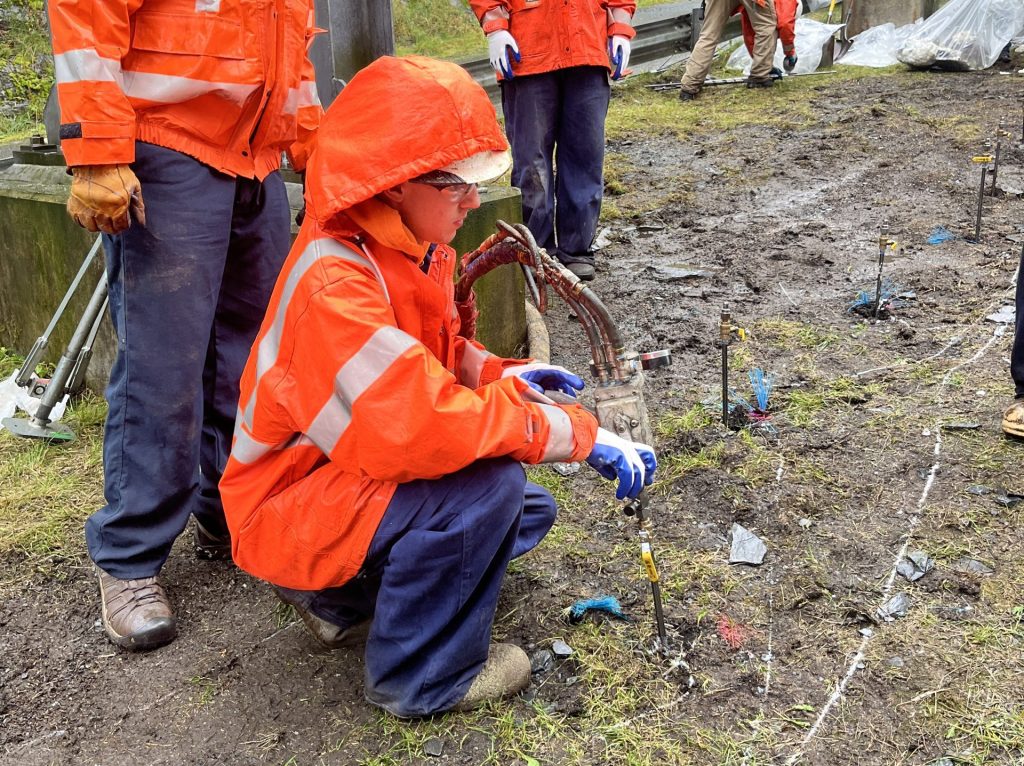
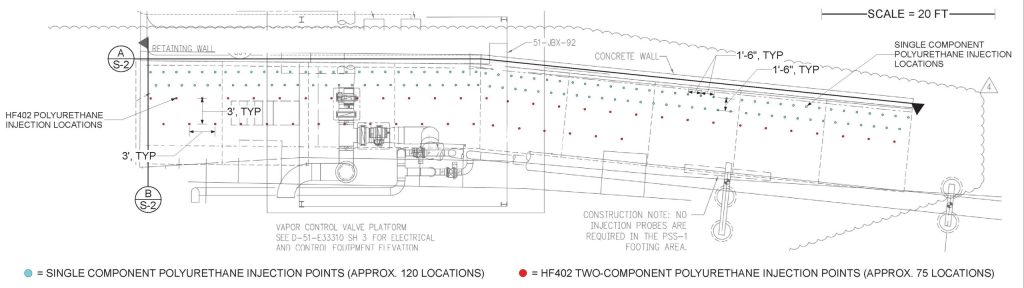


The dual-grout method successfully stabilized the distressed retaining wall without requiring excavation or demolition. The combination of HS010 for precision void filling and HF402 for bulk soil improvement allowed the contractor to achieve stabilization objectives while maintaining structural integrity and minimizing risk to on-site infrastructure.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the
Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Services apply.
In 2 days, we will teach you what you need to know to successfully tackle soil improvement projects!
4466 Custer Street
Manitowoc, WI 54220